What you can expect
The exam requires removing jewelry, glasses and clothing above the waist. You'll be asked to change into a hospital gown.
A CT coronary angiogram is usually done in the radiology department of a hospital or an outpatient imaging facility.
Before a CT coronary angiogram, you may receive a medication called a beta blocker to slow your heart rate. Doing so provides clearer images on the CT scan. Let your health care provider know if you've had side effects from beta blockers in the past.
You might also be given nitroglycerin to widen (dilate) your coronary arteries.
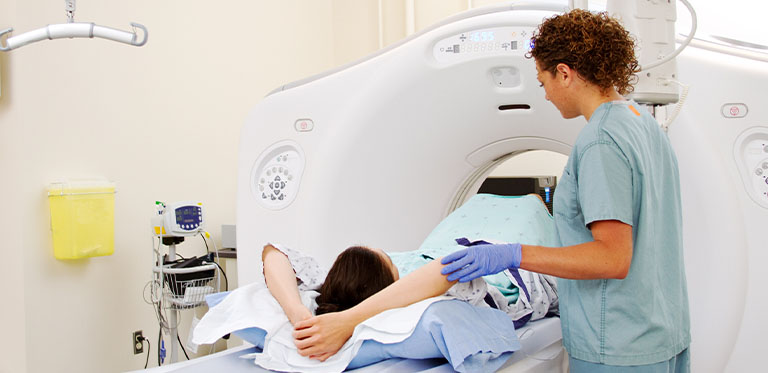
During the exam
A technologist or nurse will insert an IV into the hand or arm. The dye or contrast media flows through this IV. The dye helps blood vessels show up better on the CT images. You'll also have sticky patches called electrodes placed on your chest to record your heart rate.
You'll lie on a long table that slides through a short, tunnel-like machine (CT scanner).
During the scan you need to stay still and hold your breath as directed. Movement can cause blurry images.
A technologist operates the CT machine from a room that's separated from your exam room by a glass window. An intercom system allows you and the technologist to talk to each other.
Although the actual scanning portion of the test takes a few minutes, it may take up to an hour for the process to be completed.
After your CTA is completed, you can return to your normal daily activities. You should be able to drive yourself home or to work. Drink plenty of water to help flush the dye from your body.
Results
Brighton’s board-certified radiologist studies your CTA and provides the results to your doctor.
If your test suggests that you have or are at risk of heart disease, you and your provider can discuss treatment options.